Introduction
Chemical Properties
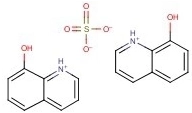
8-Hydroxyquinoline sulfate, with the chemical formula 2C9H7NO·H2O4S and CAS number 134-31-6, is a compound that presents as yellow crystalline powder. It has a molecular weight of approximately 388.4 g/mol. This substance is notably soluble in water, with a solubility of ≥10 g/100 mL at 19 ºC, making it convenient for application in aqueous solutions. It also shows solubility in methanol and is slightly soluble in ethanol, while being almost insoluble in acetone or ether. In terms of stability, it is sensitive to moisture, being hygroscopic, and thus requires proper storage conditions to maintain its effectiveness. When exposed to alkali, it can decompose, which is an important factor to consider during its handling and use.
Production and Availability
Industrially, 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate is typically synthesized through a series of chemical reactions involving the starting material 8-hydroxyquinoline. The production process requires precise control of reaction conditions, including temperature, pressure, and reagent concentrations, to ensure high purity and yield. Commercially, it is available in various forms, often as a powder, which can be easily dissolved or mixed according to specific application requirements. When purchasing 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate, it is crucial to source it from reliable suppliers. One should look for products that meet certain quality standards, such as having a specified purity level, usually above 97% as per industry norms. Reputable chemical suppliers will provide detailed product specifications, including information on impurities, solubility, and storage instructions. It is also important to ensure compliance with local regulations regarding the purchase and use of such chemicals, as improper handling or use of substandard products can lead to ineffective results or potential harm to plants and the environment.
The Primary Uses in Agriculture

As a Fungicide
One of the most prominent uses of 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate in agriculture is as a fungicide. It exhibits significant efficacy against a wide range of fungal diseases that can plague crops. The compound works by interfering with the metabolic processes of fungi. Its chemical structure allows it to penetrate the fungal cell walls and disrupt essential functions such as respiration and nutrient uptake. This ultimately leads to the inhibition of fungal growth and reproduction, preventing the spread of diseases. In the case of common crop diseases like powdery mildew, which affects a variety of plants including cucurbits and grains, 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate can be applied as a foliar spray. For vineyards dealing with downy mildew, a preventive spray program using this compound can help safeguard the grapevines. When used as a fungicide, the appropriate dosage and application frequency are crucial. Typically, for foliar applications, a concentration ranging from 0.1% to 0.5% of the active ingredient in water is recommended, depending on the severity of the infestation and the crop type. Application should be carried out during periods of low wind and preferably in the early morning or late evening to minimize evaporation and ensure maximum contact with the plant surfaces.
In Soil Treatment
In the realm of soil management, 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate plays a vital role. It can influence the soil microbial community in beneficial ways. By selectively inhibiting certain harmful soil-borne fungi and bacteria, it helps create a more balanced microbial ecosystem. This, in turn, promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms that contribute to nutrient cycling and plant root health. For instance, in soils prone to root rot diseases caused by Fusarium or Pythium species, the application of 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate can suppress the growth of these pathogens. Additionally, it has the property of chelating heavy metals present in the soil. In contaminated soils, it can bind with metals like copper, zinc, and lead, reducing their bioavailability and preventing their uptake by plants. This not only protects the plants from metal toxicity but also aids in the remediation of polluted soils. When used for soil treatment, it can be incorporated into the soil at a rate of around 5 to 10 kilograms per hectare, depending on the initial soil quality and the level of contamination or disease pressure.
Seed Treatment
Seed treatment with 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate offers a preemptive strike against various challenges that seeds face during germination and early growth stages. The compound forms a protective layer around the seeds, safeguarding them from fungal infections that could otherwise lead to seed rot and poor germination. It also has the potential to enhance seed vigor and germination rates. This is achieved through its influence on seed metabolism. By providing a microenvironment rich in essential nutrients and protecting against pathogens, it gives the seeds a better chance to sprout and establish healthy seedlings. In the case of cereal seeds, such as wheat and barley, treating them with a solution containing 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate at a concentration of about 0.2% to 0.3% can significantly improve germination percentages and reduce the incidence of damping-off diseases. The treatment can be carried out by soaking the seeds in the prepared solution for a specific duration, usually 6 to 12 hours, before sowing. This ensures that the seeds are adequately coated and primed for a successful start to their growth cycle.
The Primary Uses in Horticulture
Cut Flower Preservation
In the world of floriculture, 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate is a key ingredient in many commercial cut flower preservatives. When cut flowers are severed from their plants, they lose their natural source of water and nutrients, and are also more susceptible to microbial attack. The sulfate compound helps in multiple ways. Firstly, it acts as a potent antibacterial and antifungal agent, preventing the growth of microbes in the vase water. This is crucial as bacteria and fungi can clog the xylem vessels of the cut stems, impeding water uptake and leading to wilting. Secondly, it can chelate metal ions present in the water. By binding to metals like iron and copper, it prevents them from catalyzing oxidative reactions that can damage the flower tissues and cause premature senescence. For example, in a typical cut flower preservative formulation, a concentration of around 200 to 300 ppm of 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate, combined with sucrose and an acidifier, can significantly extend the vase life of roses, lilies, and other popular cut flowers. The preservative solution can be prepared by dissolving the required amounts of the components in distilled water and replacing the vase water with this solution every 2 to 3 days to maintain its effectiveness.
Potted Plant Care
For potted plants, whether they are ornamental foliage plants or flowering varieties, 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate can offer several benefits. In the soil of potted plants, it helps control soil-borne pathogens. Fungal diseases like root rot and damping-off can be devastating for potted plants, especially in the confined environment of a pot. By periodically applying a diluted solution of 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate to the soil, the growth of harmful fungi can be suppressed. Additionally, it can enhance the plant's nutrient uptake. It does this by interacting with the soil particles and making certain micronutrients more available to the plant roots. For instance, in a study on African violets, plants treated with a soil drench containing 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate at a low concentration showed improved growth, with darker green leaves and more prolific blooming. The treatment can be carried out once every 2 to 3 months during the growing season, depending on the plant species and the pot size, to keep the plants healthy and thriving.
Garden Disease Prevention
In outdoor gardens, a wide array of diseases can threaten the health and aesthetics of plants. 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate can be used as a preventive measure. It can be sprayed on plants, especially those that are prone to fungal infections during periods of high humidity or when new growth is emerging. For example, in a rose garden, spraying a solution with 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate before the onset of the rainy season can protect the plants from black spot and powdery mildew. In a vegetable garden, it can safeguard plants like tomatoes and cucumbers from early blight and downy mildew. The spray solution should be carefully prepared, usually with a concentration of 0.2% to 0.4% of the active ingredient, and applied evenly on both sides of the leaves and stems. This creates a protective barrier that inhibits the attachment and penetration of fungal spores, helping to maintain the lushness and beauty of the garden throughout the growing season.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate plays a multifaceted and crucial role in both agriculture and horticulture. Its applications as a fungicide, in soil treatment, for seed protection, in cut flower preservation, potted plant care, and garden disease prevention have the potential to enhance plant health, increase yields, and beautify our landscapes. However, it is imperative that users approach its application with a sense of responsibility, strictly adhering to safety guidelines to protect the environment, consumers, and the plants themselves. As research continues to unfold, we can anticipate even more refined and innovative uses of this compound, further solidifying its place as an essential tool in the cultivation and care of plants. With proper usage, 8-hydroxyquinoline sulfate can contribute to the sustainable growth and prosperity of the agricultural and horticultural sectors for years to come.











