Introduction

In a bustling chemical research laboratory, two chemists were conducting an experiment to develop a new type of high - efficiency catalyst for the petroleum industry. They were using ammonium molybdate as a key component. One batch of ammonium molybdate they used was of a relatively low - purity grade, while the other was a high - purity one. To their surprise, the results of the two experiments were strikingly different. The catalyst made from the high - purity ammonium molybdate showed excellent catalytic activity, significantly accelerating the reaction rate, while the one from the low - purity sample had much lower efficiency and even some unexpected by - products. This real - world scenario raises a crucial question: What are the standard purity grades of ammonium molybdate available, and how do they influence its effectiveness in various applications?
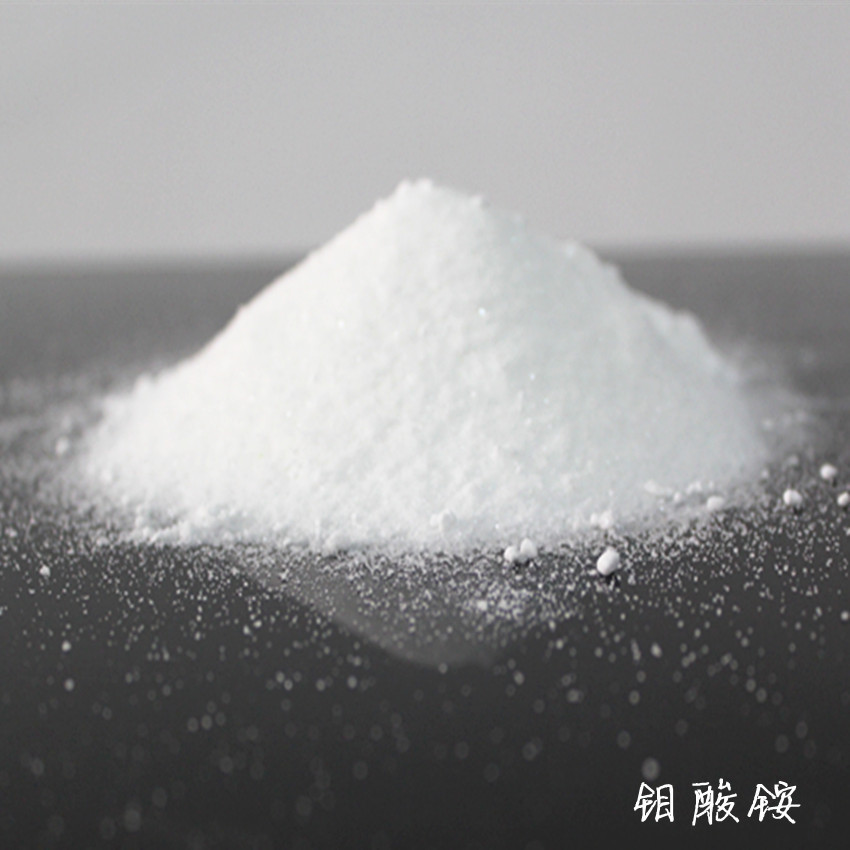
Ammonium molybdate, with the chemical formula often represented as \((NH_{4})_{6}Mo_{7}O_{24}\cdot4H_{2}O\), is a white crystalline powder that is highly soluble in water. It plays a vital role in a wide range of industries, from being a catalyst in the petroleum industry to a key ingredient in the production of pigments, ceramics, and even in some medical applications. The purity of ammonium molybdate can vary significantly, and these different purity grades have a profound impact on its performance and the quality of the end - products in which it is used. Understanding these purity grades and their effects is essential for industries to optimize their processes and products.
Standard Purity Grades of Ammonium Molybdate
1. Technical Grade
Technical grade ammonium molybdate typically has a purity range of approximately 80 - 90%. It contains a relatively high amount of impurities. In industries where high - purity substances are not strictly required, such as in common metal surface treatment processes, it can be used to form a protective layer on metal surfaces. For example, in some simple metal - working factories, technical - grade ammonium molybdate is used in solutions to treat metal parts, enhancing their corrosion resistance to a certain extent. It is also used in the synthesis of some basic chemical raw materials, like in the production of certain low - end fertilizers where the presence of a few impurities does not significantly affect the overall function.
2. Reagent Grade
Reagent grade ammonium molybdate offers a higher purity level, usually ranging from 95 - 98%. The impurity content is much lower compared to the technical grade. In laboratory settings, where accurate and reliable results are crucial for scientific research and analysis, reagent - grade ammonium molybdate is the go - to choice. For instance, when chemists are conducting routine chemical analysis tests to determine the composition of a sample or when performing small - scale fine chemical synthesis experiments, the use of reagent - grade ammonium molybdate ensures that the reactions are not interfered with by excessive impurities. This high - purity grade helps in obtaining consistent and accurate experimental data, which is essential for the development of new chemical compounds and the understanding of chemical reactions.
3. High - Purity Grade
High - purity grade ammonium molybdate has a purity of 99% or even higher, with negligible amounts of impurities. In the manufacturing of high - end electronic materials, such as in the production of semiconductor devices, high - purity ammonium molybdate is indispensable. The extremely low impurity level ensures the high - performance and reliability of electronic components. For example, in the preparation of some advanced catalysts used in the petrochemical industry for highly selective reactions, high - purity ammonium molybdate is used as a key ingredient. These catalysts need to have precise chemical compositions to function effectively in promoting specific chemical reactions, and the high - purity ammonium molybdate enables the production of catalysts with the required quality and performance.
Influence on Effectiveness in Various Applications

1. In Catalysis
In the field of catalysis, such as in the petroleum industry and organic synthesis, the purity of ammonium molybdate plays a crucial role. High - purity ammonium molybdate, like the 99%+ grade, provides more stable and efficient catalytic activity. In petroleum refining processes, high - purity ammonium molybdate - based catalysts are used to promote reactions like hydrodesulfurization, which is essential for reducing the sulfur content in fuels. The high purity ensures that the active sites of the catalyst are not poisoned by impurities, leading to a longer catalyst lifespan and higher reaction selectivity. For example, in the production of high - quality diesel fuel, high - purity ammonium molybdate catalysts can effectively remove sulfur compounds, meeting the strict environmental standards for fuel quality. In contrast, low - purity ammonium molybdate, such as the technical grade, may contain impurities like heavy metals or other chemical substances. These impurities can interfere with the catalytic reaction, reducing the catalyst's activity and selectivity. They may also cause the catalyst to deactivate more quickly, requiring more frequent catalyst replacements, which increases production costs.
2. In Metallurgy
In metallurgy, especially in metal smelting and alloy manufacturing, the purity of ammonium molybdate directly affects the quality of the final products. When producing molybdenum - containing alloys, high - purity ammonium molybdate ensures a uniform distribution of molybdenum in the alloy matrix. For instance, in the production of high - strength steel alloys where molybdenum is added to enhance strength and corrosion resistance, high - purity ammonium molybdate as a source of molybdenum allows for precise control of the alloy composition. This results in alloys with consistent mechanical properties, making them suitable for applications in aerospace and automotive industries. On the other hand, low - purity ammonium molybdate can introduce impurities into the alloy. These impurities can disrupt the crystal structure of the alloy, leading to uneven mechanical properties. In extreme cases, they can cause defects such as cracks or porosity in the alloy, reducing its strength and durability. For example, in the casting of metal parts, if low - purity ammonium molybdate is used, the resulting alloy parts may have a higher risk of failure under stress.
3. In Agriculture
In agriculture, ammonium molybdate is used as a source of the essential micronutrient molybdenum in fertilizers. The purity of ammonium molybdate in these fertilizers impacts the efficiency of molybdenum uptake by plants. A suitable purity level, often in the reagent - grade range, ensures that plants can effectively absorb molybdenum. Molybdenum is involved in various enzymatic reactions in plants, such as nitrogen fixation in legumes and the metabolism of nitrogen - containing compounds. For example, in soybean fields, applying fertilizers with the right - purity ammonium molybdate can enhance the activity of nitrogen - fixing bacteria in the root nodules of soybeans. This leads to increased nitrogen fixation, providing more nitrogen for the plants, and ultimately resulting in higher yields and better - quality soybean crops. If the ammonium molybdate in fertilizers has a low purity, it may contain contaminants that can be harmful to plants or interfere with the uptake of molybdenum. This can lead to molybdenum deficiency in plants, causing stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and reduced crop yields.
Conclusion
n conclusion, ammonium molybdate comes in different standard purity grades, each with its own characteristics. Technical grade, with 80 - 90% purity, serves well in industries with less strict purity requirements like basic metal surface treatment and low - end fertilizer production. Reagent grade, having 95 - 98% purity, is essential for laboratory - based scientific research and analysis, ensuring accurate results. High - purity grade, 99%+ pure, is crucial in high - tech fields such as electronics and the production of high - end catalysts.
The purity grade of ammonium molybdate significantly influences its effectiveness in various applications. In catalysis, high - purity grades lead to more efficient and stable catalytic reactions, while low - purity ones can reduce catalyst performance. In metallurgy, high - purity ammonium molybdate is necessary for producing high - quality alloys, and low - purity can cause defects in the alloy. In agriculture, the right - purity ammonium molybdate in fertilizers promotes plant growth, and low - purity can lead to nutrient deficiencies.
It is of utmost importance to select the appropriate purity grade of ammonium molybdate according to specific application requirements. This not only ensures the quality and performance of the final products but also helps in optimizing production processes and reducing costs. As industries continue to evolve and demand more advanced materials and processes, further exploration and research into the properties and applications of different purity grades of ammonium molybdate are encouraged. This will enable us to unlock more potential uses and improvements in various fields, from enhancing the efficiency of chemical reactions to improving the quality of agricultural products.













